How to Identify Authentic Autographs

Verification in Aviation: Ensuring Safety
Rigorous verification processes are crucial in the aviation industry to minimize risks and ensure the safety of passengers and crew. These processes encompass a wide range of activities, from the design and manufacturing stages of aircraft components to the maintenance and operation of the final product. Thorough verification helps identify potential flaws and vulnerabilities early on, mitigating the likelihood of catastrophic failures in flight.
Verification is not a single event but rather an ongoing process that involves multiple stakeholders. From engineers and technicians to pilots and maintenance personnel, everyone plays a crucial role in upholding the highest standards of safety.
Design and Manufacturing Verification
Aircraft design and manufacturing processes must undergo stringent verification procedures. This includes rigorous testing and inspections at each stage of production to ensure that components meet the required specifications and standards. These checks are critical in identifying any deviations from the design blueprints, preventing errors that could compromise the structural integrity or operational efficiency of the aircraft.
Testing methodologies employed during verification can range from simulations and computer modelling to physical prototypes and flight tests. This comprehensive approach aims to identify and rectify potential issues before they lead to costly and potentially hazardous consequences.
Maintenance and Operational Verification
Regular maintenance and operational verification are essential for maintaining the safe operation of aircraft. These procedures ensure that the aircraft is always in optimal condition and capable of performing its intended function without risk. This includes checks on all systems, components, and procedures to confirm their readiness for flight.
Implementing these procedures involves employing specialized tools and techniques for analyzing data, making critical decisions, and addressing any identified issues swiftly and efficiently. This ensures that the aircraft remains compliant with safety regulations and industry best practices.
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Verification procedures in aviation are heavily influenced by stringent regulatory bodies and industry standards. These guidelines ensure that aircraft and associated operations adhere to safety protocols and minimize the risks associated with flight.
Compliance with these standards is paramount for maintaining public trust and ensuring the safety of the aviation ecosystem as a whole. These standards are continuously updated to reflect advancements in technology and operational practices, ensuring that verification procedures remain effective and relevant.
Human Factors in Verification
Human factors play a critical role in the aviation verification process. Training and certification of personnel are paramount for ensuring that individuals are equipped with the knowledge and skills to perform verification tasks accurately and efficiently. Human error can be a significant contributor to safety issues, and effective verification procedures must account for this possibility.
Effective communication and collaboration between various personnel involved in the verification process are vital to avoid misinterpretations and ensure that everyone understands their roles and responsibilities. Continuous improvement and feedback mechanisms are essential to enhance the overall verification process.
Examining the Signature's Context: Beyond the Script Itself
Understanding the Historical Context
Examining a signature's historical context is crucial for authenticating it. This involves researching the individual's known activities, societal norms, and potential forgeries during that specific period. Did the signer have any known imitators? Were there specific social or political pressures that could have motivated a forgery? Understanding the circumstances surrounding the document's creation provides vital clues to its authenticity, moving beyond a simple analysis of the script itself.
A historical analysis often reveals details about the signer's habits and how their signature might have evolved over time. For example, variations in penmanship could be attributed to age, health, or changes in writing instruments. These subtle changes offer valuable insights into the document's authenticity, suggesting whether the signature aligns with known patterns for that individual.
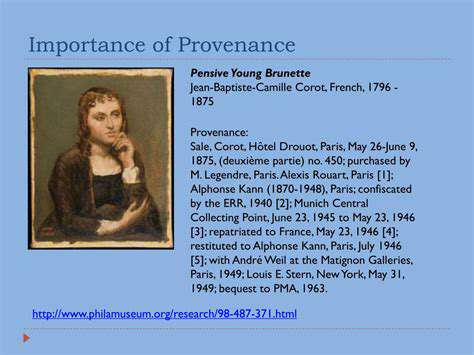
Analyzing the Document's Provenance
The document's provenance—its history of ownership and custody—plays a significant role in authenticity. A documented chain of custody, demonstrating how the document has been handled and stored over time, can significantly strengthen its legitimacy. This includes records of transfers, acquisitions, and any known alterations or repairs to the document itself.
Tracing the document's journey through various hands can reveal potential points of compromise or manipulation. If there are unexplained gaps or inconsistencies in the provenance, it raises questions about the document's authenticity and requires further investigation. The document's history adds layers of context, allowing examiners to evaluate the likelihood of forgery or misrepresentation.
Evaluating the Signature's Physical Characteristics
Beyond the script itself, the physical characteristics of the signature are key indicators. Look for ink consistency, pen pressure variations, and the overall style and flow of the signature. Do these match the known characteristics of the signer's handwriting? A sudden change in style or unusual characteristics could point to a forgery.
Considering the Signature's Placement and Surroundings
The position of the signature on the document provides clues. Is the signature in the typical location for this type of document? Is the signature positioned in a way that looks natural or forced? The signature's placement in relation to other elements of the document, such as text, seals, or dates, can be telling indicators of authenticity or potential alterations.
Comparing to Known Samples
A crucial step in authenticating a signature is comparing it to known authentic samples of the signer's handwriting. These samples should ideally be from the same period as the disputed document. Experts can then look for similarities and discrepancies in the script, pen pressure, and other characteristics. This comparison provides a strong basis for determining whether the signature aligns with the signer's known patterns.
Scrutinizing the Supporting Evidence
Beyond the signature itself, consider the supporting evidence surrounding the document. Are there witnesses who can attest to the signing? Are there other corroborating documents or records that support the authenticity of the document? The existence and reliability of such evidence can greatly influence the determination of authenticity. This includes assessing the credibility of witnesses and the overall consistency of the supporting material with the signature itself. Thoroughly scrutinizing the supporting evidence is essential for a comprehensive evaluation.
Visual Clues and Stylistic Analysis: Identifying Subtle Differences
Visual Clues in Artistic Representations
Analyzing visual cues is paramount in identifying subtle differences within artistic representations. Close observation of brushstrokes, color palettes, and the overall composition can reveal nuances in style and intent. For example, a painter's choice of a vibrant, almost chaotic color palette might suggest a different emotional tone compared to a more muted, subdued approach. These subtle variations are often missed by the casual observer but can be key to understanding the artist's perspective and the era in which the work was created.
Beyond color and brushwork, the arrangement of figures, objects, and space within the artwork can provide valuable insights. A disproportionate scale or unusual placement of elements might suggest a deliberate attempt to convey a specific message or mood. Examining the interplay of light and shadow, and how it impacts the subject matter, can also reveal important details about the artist's intentions and the context of the artwork.
Stylistic Analysis: Deconstructing the Artist's Hand
Stylistic analysis delves deeper into the characteristics that define an artist's unique approach. This includes studying the artist's consistent use of line, form, and texture. Identifying recurring patterns in composition, subject matter, or treatment of light and shadow can provide a strong basis for distinguishing between different styles or periods.
Examining the artist's choices in materials and techniques can also be very revealing. Was oil paint used, or watercolor? Did the artist favor a loose, gestural style, or a meticulous, detailed approach? These choices often reflect the artist's personal preferences, technical skills, and the prevailing artistic trends of their time.
Identifying Subtle Differences in Composition
Compositional elements are crucial for understanding the impact and message of a piece of art. A slight shift in the placement of figures or objects can significantly alter the perceived balance and emphasis within the artwork. Careful observation of the focal point, the background, and the overall arrangement of elements will help to uncover these subtle differences.
The Role of Light and Shadow in Visual Analysis
Light and shadow are powerful tools in an artist's arsenal for creating depth, mood, and form. Paying close attention to how light interacts with the subject matter can reveal the artist's intentions and the atmosphere they aim to convey. An artist might use light to highlight certain features, or to cast dramatic shadows that draw attention to specific elements.
Contextual Clues: Understanding the Historical and Cultural Factors
Understanding the historical and cultural context surrounding the artwork is essential for identifying subtle differences and interpreting its true meaning. Artistic styles often reflect the prevailing social and political climates of the time. Consider the artist's background, the cultural values of the era, and the potential influences from other artistic movements or traditions.
The Impact of Patronage and Intended Audience
The intended audience and the patron who commissioned the work can also play a role in the subtle differences observed in artworks. Understanding the preferences of the patron or the societal expectations of the time can shed light on the artist's decisions and the intended message of the piece. Did the patron request specific subjects or styles? Was there a particular message the patron sought to convey through the artwork? These factors can influence the artwork's visual characteristics in subtle but significant ways.
Seeking Professional Expertise: The Final Step in Authentication
Understanding the Importance of Professional Expertise
Seeking professional expertise is a crucial final step in authentication, especially when dealing with potentially valuable or sensitive items. Professional authentication services, whether for art, antiques, documents, or other collectibles, bring specialized knowledge and experience to bear. This expertise transcends the typical knowledge base of a layperson, enabling a more thorough and accurate assessment of authenticity.
Professional experts possess a deep understanding of historical contexts, manufacturing processes, and stylistic nuances. This detailed knowledge allows them to identify subtle indicators of forgery or imitation that might be missed by someone without the specialized training and experience. Their perspective is critical in determining the true origins and value of the item in question.
Evaluating the Credentials of Authentication Professionals
Not all authentication professionals are created equal. When seeking expert opinion, it's vital to thoroughly vet the qualifications and experience of the individual or organization offering the service. Researching their background, publications, and affiliations is essential. Look for established credentials, professional certifications, or membership in relevant associations.
Checking for a track record of successful authentication cases can provide further insight. A reputable professional will likely have a portfolio or case studies available. Be cautious of individuals or organizations claiming expertise without demonstrable experience or qualifications.
Considering the Scope of Authentication Services
Different authentication services cater to diverse needs. Some professionals specialize in specific fields, like fine art, while others might have expertise in historical documents or antiques. Understanding the precise scope of the service offered by a potential expert is crucial.
For example, an art authentication service might focus on paintings, sculptures, or prints, while a document authentication service will likely focus on historical records, signatures, or provenance. Knowing the specific area of expertise is essential before entrusting the item for authentication.
Methods Employed by Authentication Professionals
Professional authentication often involves a combination of visual inspection, historical research, scientific analysis, and comparison with known examples. These methods vary depending on the item being authenticated. For example, scientific analysis, such as carbon dating or material analysis, might be employed for antique artifacts. Visual comparison with known examples from the same period or maker is crucial for determining authenticity in many cases.
The Role of Documentation and Provenance
Professional authentication often requires meticulous documentation. Experts will scrutinize existing documentation, including historical records, provenance, and previous ownership details. These records provide valuable context for understanding the item's history and potential authenticity. Thorough documentation is a critical part of the authentication process and often forms a significant part of the final report.
A professional report will typically include detailed findings, analysis, and conclusions, along with supporting evidence. This documentation is invaluable for establishing the authenticity of the item for future reference and potential resale.
The Cost and Time Commitment of Professional Authentication
Professional authentication services come with a cost, which varies depending on the complexity of the item and the expertise required. It's essential to understand the associated fees and time commitment before engaging a professional. Factors such as the item's condition, the demand for the service, and the expertise involved all contribute to the price.
Furthermore, the turnaround time for authentication can vary. Some services might offer expedited options, but others might take a considerable amount of time. Be prepared to allow sufficient time for the professional to complete their assessment and provide a comprehensive report.
Read more about How to Identify Authentic Autographs
Hot Recommendations
-
*Best Sci Fi Books to Read in 2025
-
*How to Start a Reading Journal
-
*Guide to Collecting Vinyl Records by Genre
-
*Guide to Self Publishing Your Book
-
*Guide to Reading More Books
-
*How to Solve a Megaminx Fast
-
*Guide to Identifying Edible Plants While Hiking (Use Caution!)
-
*How to Solve a 5x5 Rubik's Cube
-
*Guide to Building Advanced Lego Structures
-
*How to Capture Star Trails Photography






![Guide to Building Plastic Models [Beginner]](/static/images/34/2025-06/MasteringtheAssemblyProcess3AStep-by-Step.jpg)